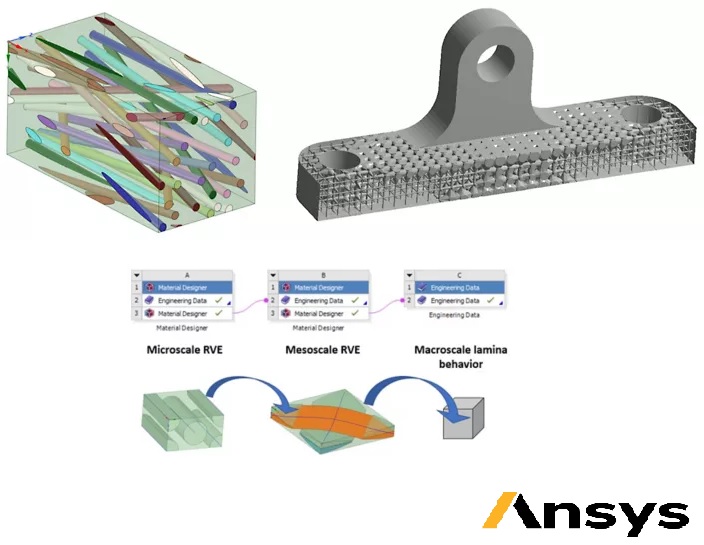
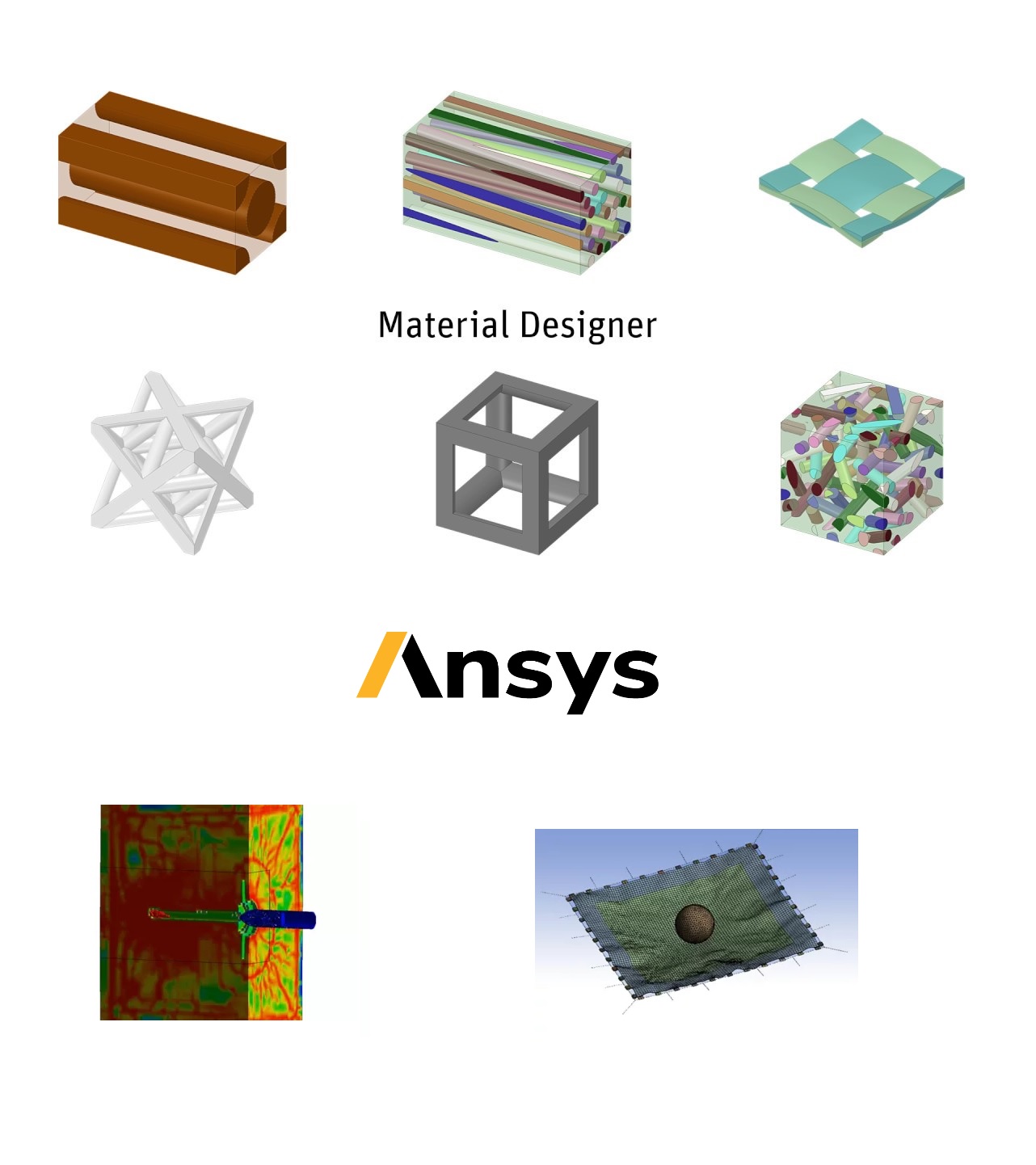
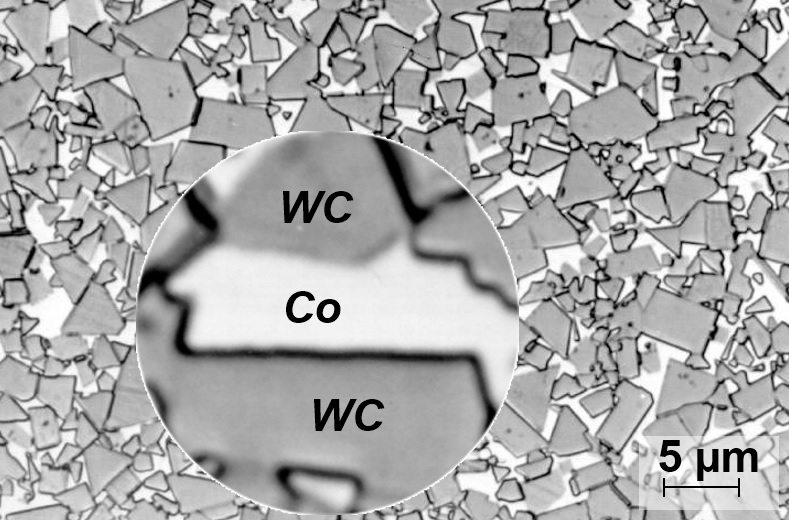
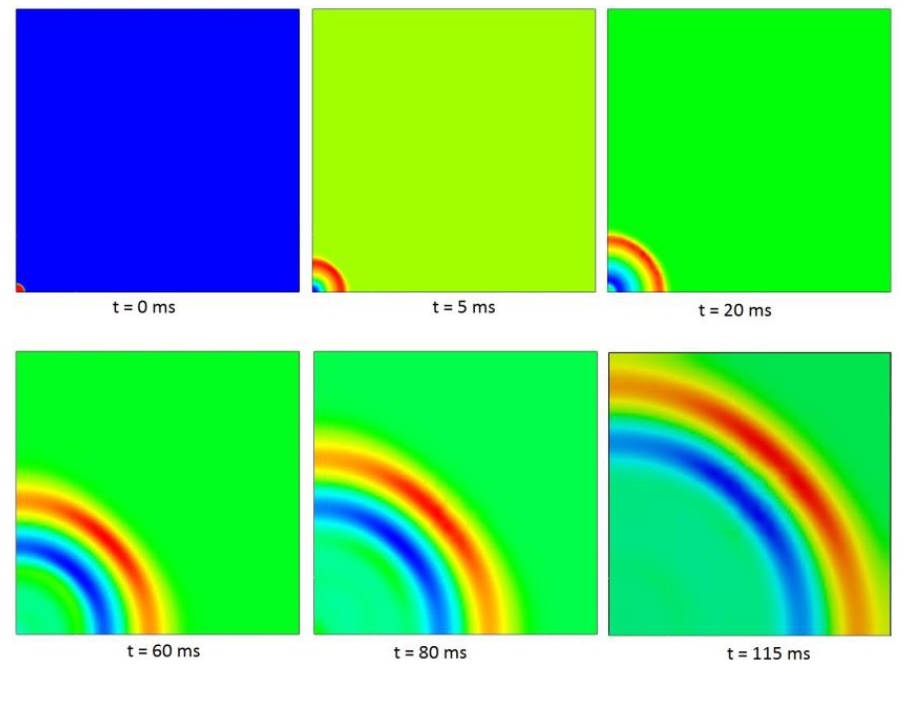
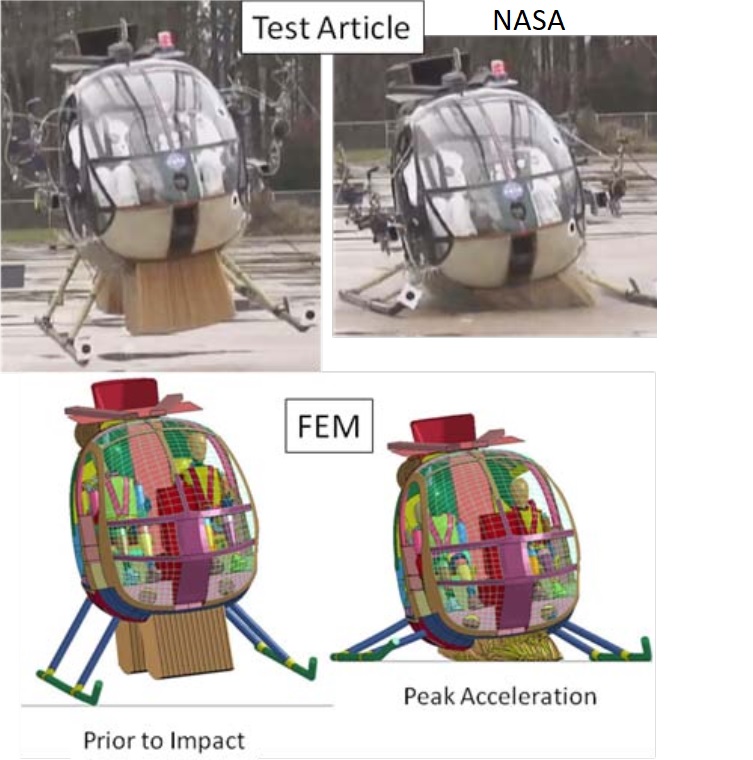
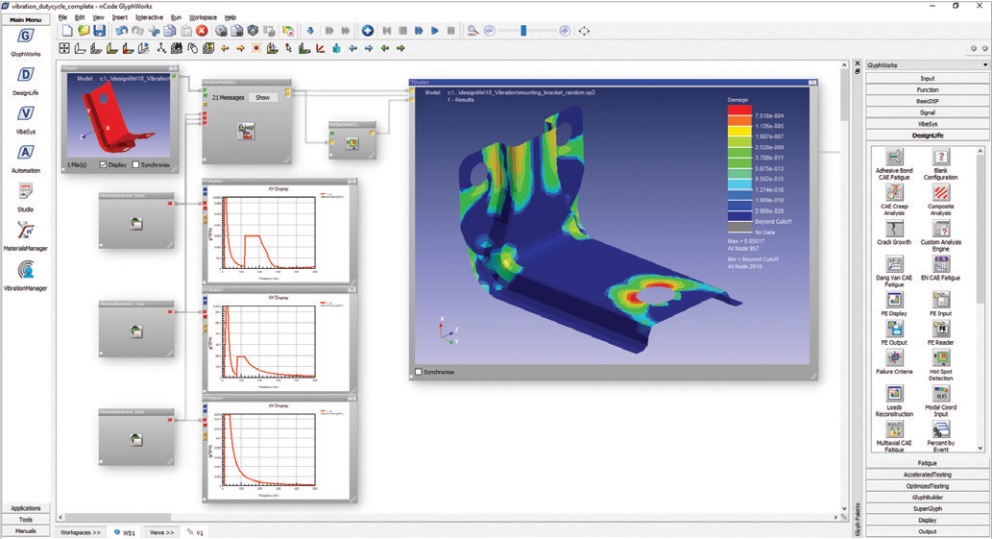
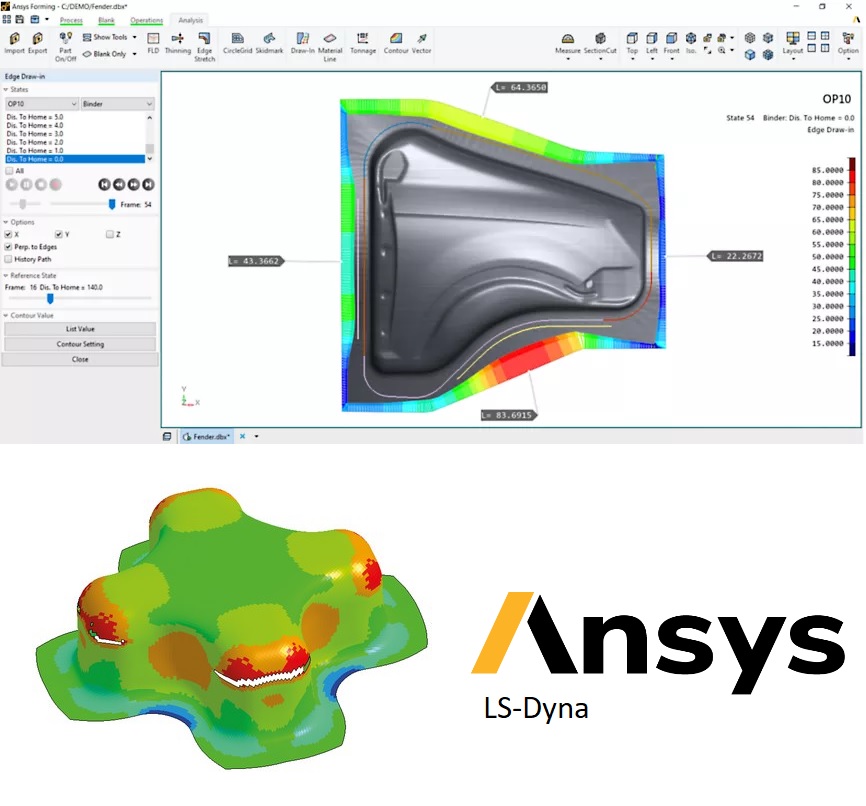
Rubber-based components, such as tires, anti-vibration systems, seals, and hoses, rely on the properties of the rubber matrix to perform their intended function. However, these properties can be significantly enhanced by embedding inclusions, such as carbon black, mica particles, or steel fibers, into the rubber matrix.
The inclusion of carbon black or mica particles into the rubber matrix is a common way to tune the material properties of rubber-based components. Carbon black, for example, can improve the wear resistance, tensile strength, and tear resistance of the rubber matrix, while mica particles can enhance the thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties.
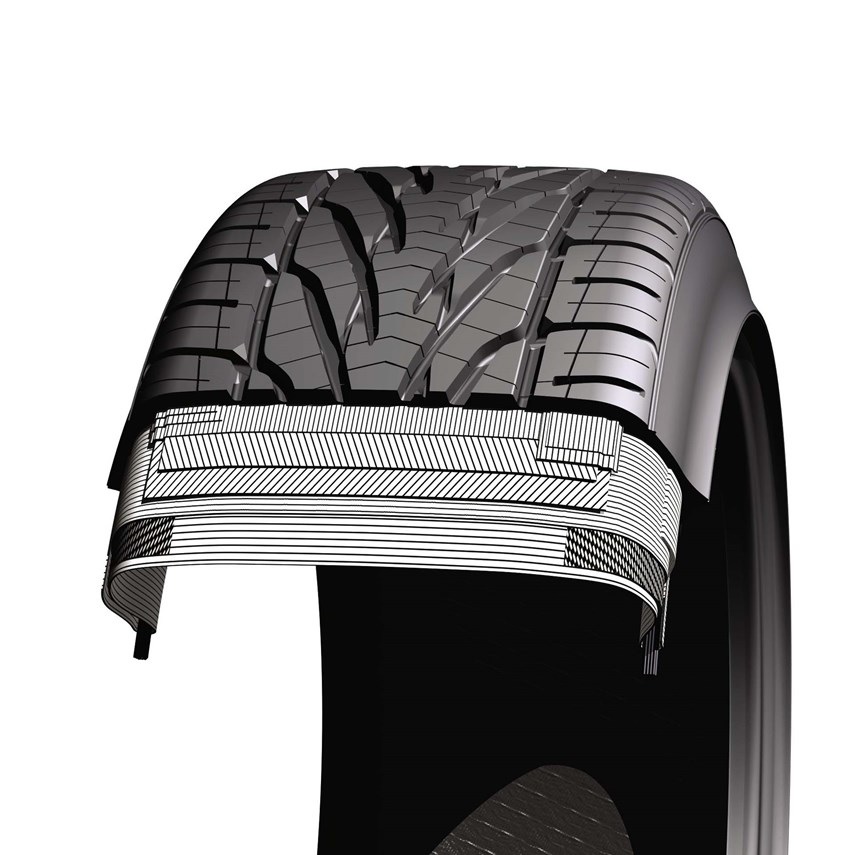
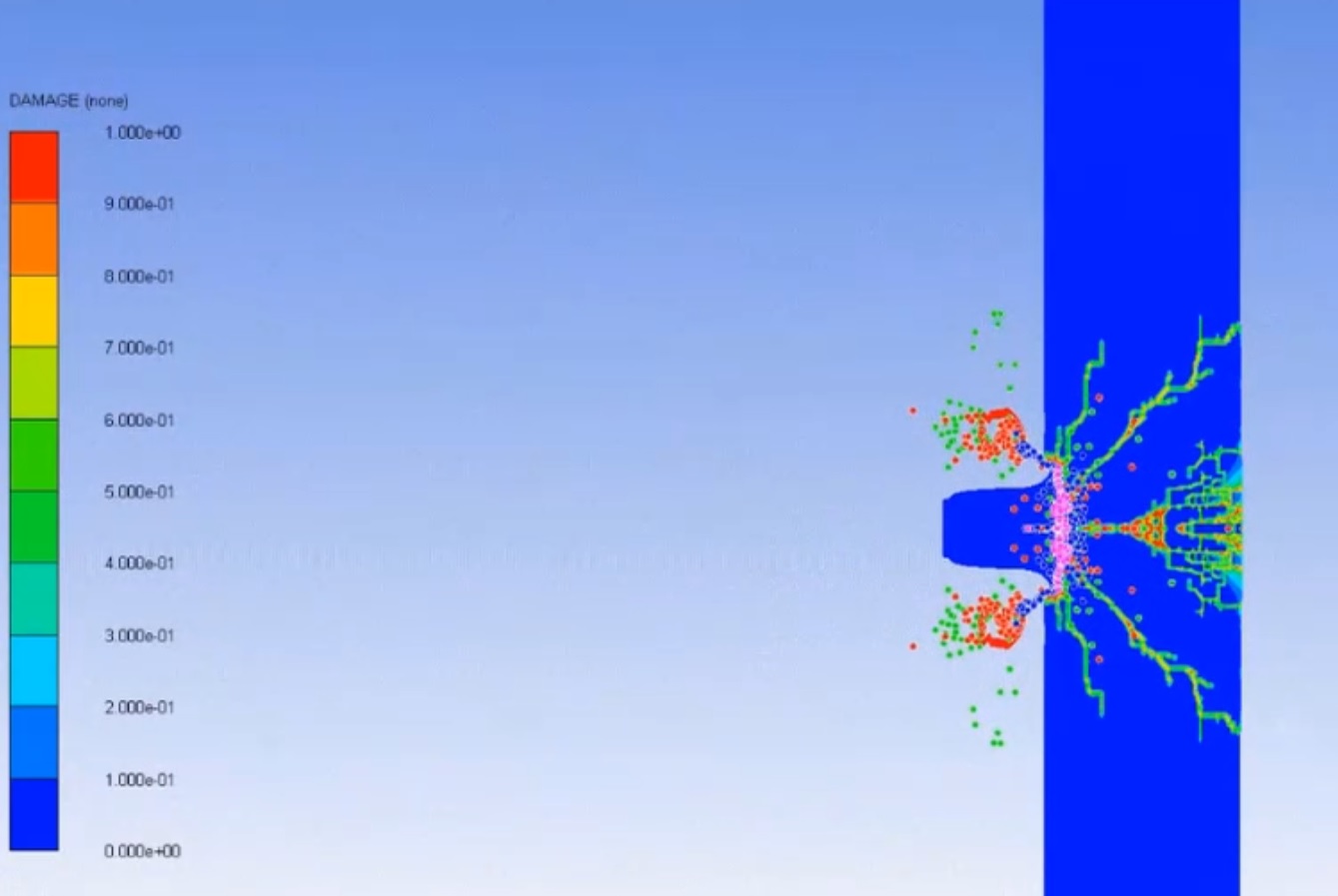
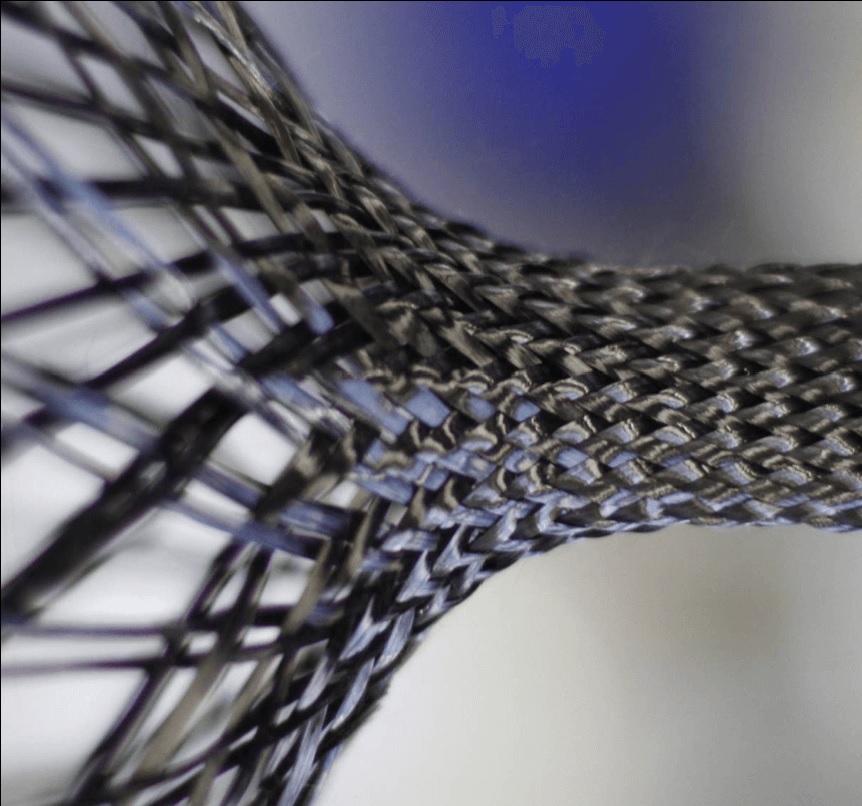
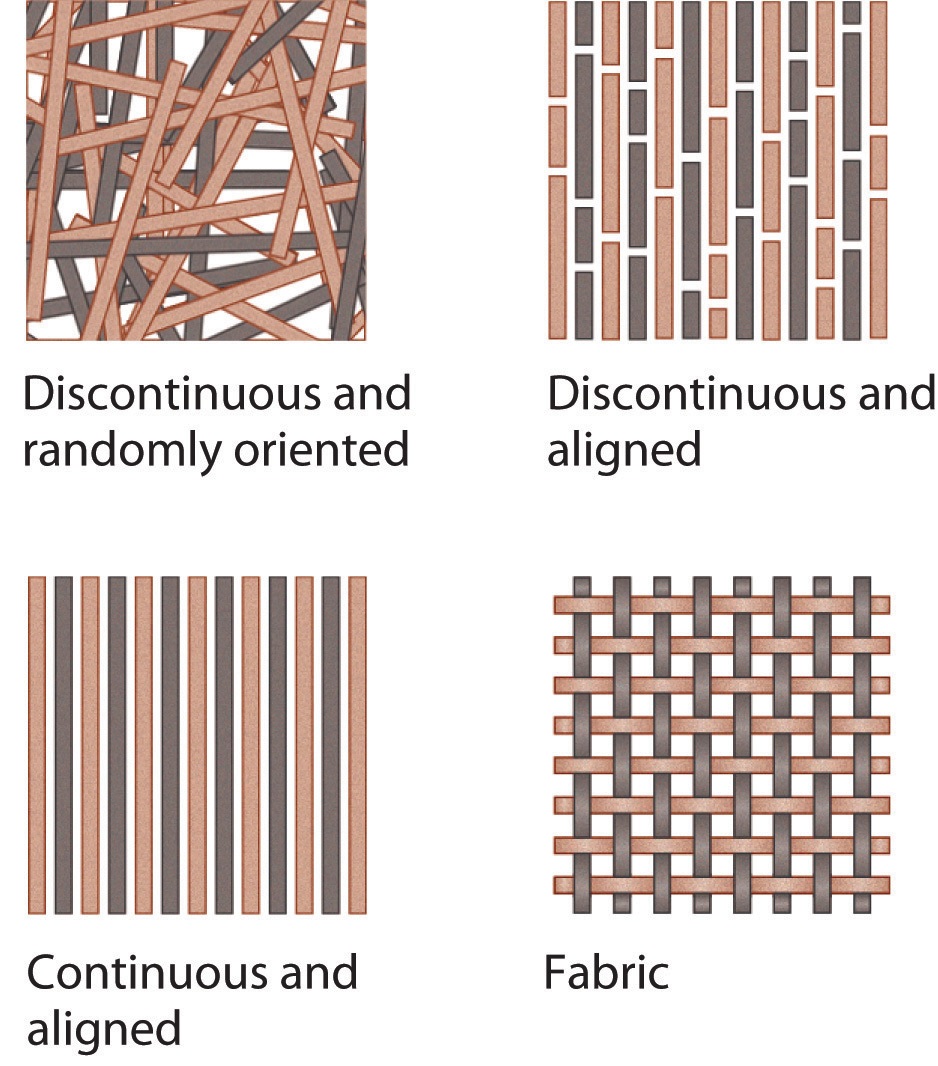
In addition to these microscopic inclusions, more complex systems like tires often contain macroscopic inclusions, such as steel fibers. These fibers are embedded into the rubber matrix in a sophisticated weave, which helps to control the footprint of the tire and enhance its performance. For example, steel fibers can improve the tire's resistance to punctures, increase its grip on wet or slippery surfaces, and enhance its overall durability and stability.