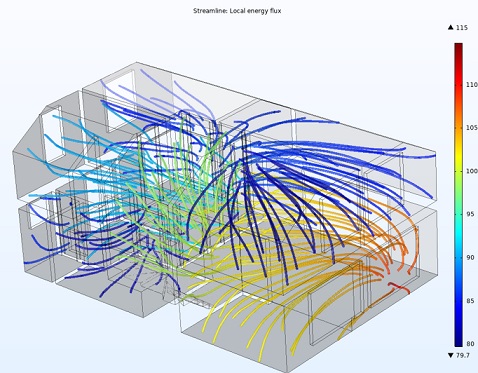
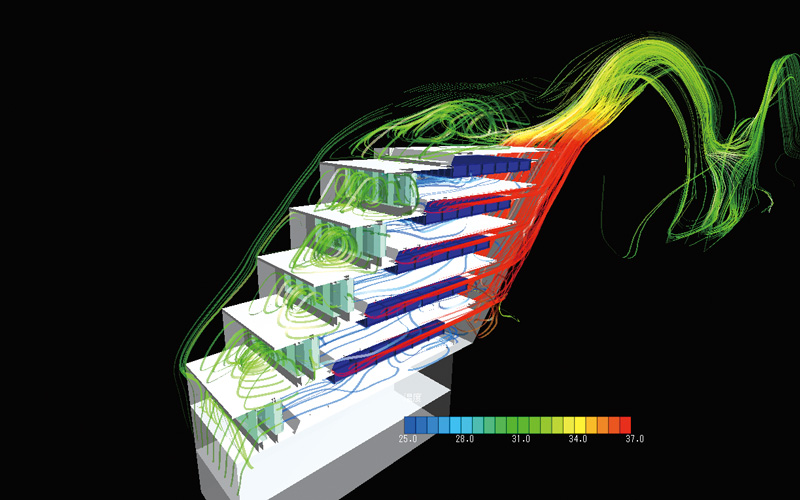
Maintaining occupant thermal comfort and indoor air quality in buildings requirs advanced HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) design. Proper ventilation plays a key role in achieving these objectives. The amount of fresh air required for ventilation depends on the size and usage of the space, as well as the number of occupants. ASHRAE Standard 62.1 provides guidelines for minimum ventilation rates for different types of spaces.
In addition to ventilation, HVAC design also involves heating and cooling systems that can regulate temperature and humidity levels within a space and remove indoor air pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon dioxide (CO2). This can be achieved through various types of equipment, such as heat pumps, boilers, and air conditioning units.
Other design considerations include insulation to reduce heat loss, glazing to control solar gain, and shading systems to minimize heat gain from direct sunlight. These elements can help to improve indoor thermal conditions and reduce the need for excessive heating or cooling.